Vehicles have been packed full of all kinds of sensors for decades now. Modern cars can barely operate without the complex network of sensors and electronics that run all the main and auxiliary systems. However, all those benefits come at a cost. Complex systems mean that there are more components that can fail.
The P0154 check engine light code is related to one of the sensors in your car, and can potentially affect the performance profile of your car. Today we’ll go over the main symptoms and causes of the P0154 code, how you can troubleshoot it on your own, and potentially how to fix the diagnosed issues.

What Is the P0154 Code, and What Does it Mean?
The P0154 code stands for “O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 2 Sensor 1).” In other words, the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) in your car has stopped receiving a signal from one of the O2 sensors in your car, specifically the one located on the exhaust system fitted to the Bank 2 of your engine. Bank 1 Vs Bank 2 can get confusing, but things become clear once you have a simple diagram in front of you.
Considering the fact that O2 sensors play a major role in helping your engine achieve optimal performance and efficiency, a loss of one sensor can cause a variety of issues, ranging from serious ones to not-so-serious ones. At the end of the day, a bad O2 sensor isn’t something you want to ignore for long.
What Is an O2 Sensor, and How Does It Work?
Modern cars are all about efficiency. Since the emissions standards were first introduced in the 1980s, all manufacturers raced to find ways of reducing toxic emissions that their cars would produce. Oxygen sensors, also known as O2 sensors or Lambda sensors, were introduced in the effort to monitor the efficiency of combustion as well as the efficiency of catalytic converters which have also become the norm around the same time.
Most modern cars have more than one O2 sensor installed on the exhaust system. The most common configuration includes an O2 sensor installed between the engine and the catalytic converter, and another one downstream of the cat. The pre-cat sensor measures how much O2 is in the exhaust gasses that leave the combustion chamber, while the post-cat sensor measures the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
The ECU uses this data to adjust the fuel trim by either adding or removing the amount of fuel that is mixed with the air in the intake. When one of the O2 sensors goes bad, the ECU is left without critical data and will usually default to failsafe values to keep the engine running. However, these values are rarely good enough to keep the engine operating efficiently.
P0154 Code Symptoms
Symptoms of the P0154 code are generally related to engine performance. Of course, the very first thing you will notice if this error pops up is the check engine light on your dashboard. In addition to that, you could experience the following:
- Rough idle
- Abnormally high fuel consumption
- The appearance of black smoke on the exhaust
Rough Idle
Fuel trim is an important metric for any engine. The moment you start your car, the fuel trim values adapt to the current needs of the engine. The trim will be different for a cold engine and one that has been running for hours on the freeway.
Similarly, your idle fuel trim will depend on the operating conditions your car is currently experiencing. Without the information provided by the O2 sensor, there is a very real chance that your idle will be affected to a point where you might experience rough idle.
Abnormally High Fuel Consumption
Another common symptom of the P0154 code is abnormally high fuel consumption. With no info from the O2 sensor, your ECU will add more fuel to the trim than necessary, in most cases. This excess fuel consumption is enough to increase your fuel expenditures. In severe cases, you can expect a proper hit on your wallet.
Black Smoke on the Exhaust
All that extra fuel we’ve just mentioned is unlikely to be efficiently burnt by the engine. Rather, most of it leaves the combustion chamber along with the exhaust smoke. Once that happens, it is vaporized and exits the exhaust in the form of black smoke.
While this symptom isn’t particularly dangerous in the short term, all this excess fuel can easily clog up your catalytic converter, or even cause damage to it. In severe cases, you could also experience detonations from an air/fuel mixture that is too rich. Detonations, no matter what causes them, can make quick work of your pistons. If you notice detonations or register engine knock issues, don’t drive the car and get the issue fixed as soon as possible.
What Causes the P0154 Error?
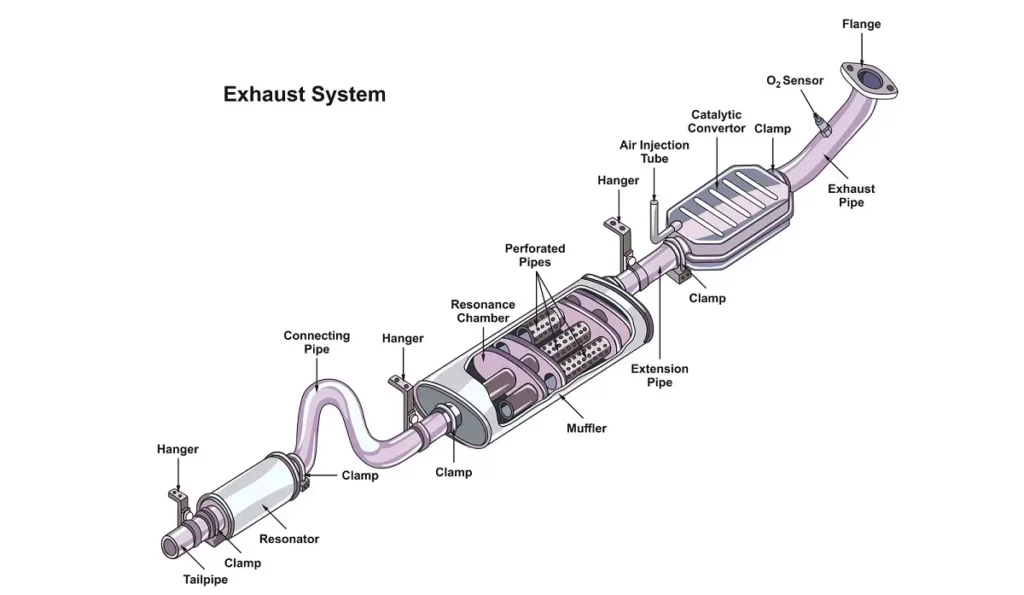
The O2 sensor is the most common culprit behind the P0154 code. There are a few other things that can go wrong, causing the O2 sensor to stop sending data to the ECU. Here’s a quick rundown of the potential causes of the P0154 error:
- Bad O2 sensor
- O2 sensor wiring issues
- Fuse Issue
- Exhaust Leaks
Bad O2 Sensor
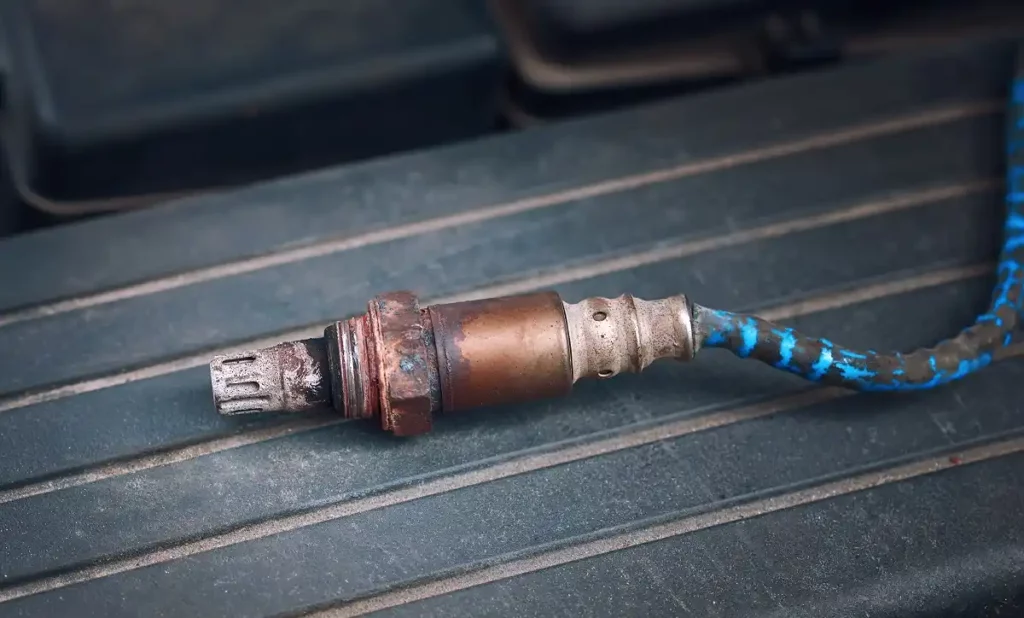
On top of the list of potential causes is a bad or malfunctioning O2 sensor. Whether it’s completely dead or stuck in high/low voltage mode, there is a good chance that an O2 sensor operating under such conditions will trip the P0154 code. That being said, the O2 failure can point to other, potentially serious issues with your engine. One of the main reasons why these sensors fail is contamination.
If your engine is consuming large amounts of engine oil, some of that oil could reach the upstream sensor (which is the relevant one for this code), and contaminate its sensor element. In this instance, replacing the sensor itself is a band-aid solution at best. You’ll need to take care of the main issue in order to put this code to rest long-term.
O2 Sensor Wiring Issues
Wiring harness issues are always a potential problem whenever you’re dealing with components that are located under the vehicle, especially ones close to the exhaust system. Since the sensor is literally mounted on the exhaust system itself, the wiring harness usually runs close to a very hot set of pipes.
Over time, the constant exposure to extreme hot/cold cycles can degrade the wiring insulation, exposing bare wires or even causing a complete break in the circuit. Any of these can cause your O2 sensor to die or stop sending info to the ECU.
Blown Fuse
A blown fuse is one of those simple things that many people tend to overlook when working on anything electrical in their cars. Your O2 sensors have their own fuses that sometimes go bad for one reason or another.
Before you start pulling things apart and replacing parts, check the fuse. It’s an inexpensive component that can be replaced very quickly and could very well solve your problem.
Exhaust Leak
Exhaust leaks are a common problem on older vehicles, or cars that are driven in the rust belt. When your exhaust system develops a leak, i.e. a hole develops somewhere along the exhaust, it will suck in additional air that your engine’s computer won’t be able to account for.
That being said, exhaust leaks usually trigger other codes that are usually related to a rich or lean condition. Having an exhaust leak trigger a P0154 code is rare, but it does happen.
How to Diagnose and Fix the P0154 Code?

Diagnosing the P0154 code will require access to the underbelly of your car. With that said, the very first thing you’ll want to do is run a full scan using an OBD II scanner. That way you’ll know what codes you’re dealing with, and whether it’s a standalone code or a mix of different codes. All of this will affect your further course of action. The next step is to check the fuse. If it’s good, proceed to inspect the following:
- O2 sensor wiring and connector
- Exhaust leaks
- O2 sensor
O2 Sensor Wiring
With a confirmed code in your scanner, find a way to safely get under the car and locate the affected O2 sensor. Follow the wiring from the sensor all the way up the car as far as you can see. You’re looking for any traces of rodent damage, insulation damage, or potentially heat damage if the wiring was touching the hot exhaust.
At this point, you can use your multimeter to check whether the wiring harness is delivering power to the sensor.
Exhaust Leaks
Exhaust leaks aren’t always that easy to find, especially if they’re small. The good news is that you’ll most likely hear an exhaust leak before you see it. Even the smallest leak will change the way your engine sounds. Common areas for exhaust leaks are any bends and joints in your exhaust system. Also, check the exhaust manifold gasket as it can fall apart over time, causing a leak. Once you’ve located the leak, make the necessary repairs.
O2 Sensor
Checking the O2 sensor means inspecting the sensor itself, but also inspecting the connector/wiring that leads to the sensors. In most cases, the sensors feature several inches of wiring that extend to the wiring harness on the car. Again, you can use the multimeter to check the resistance.
If you notice that the sensor is dead, proceed to extract it and replace it with a new one. Keep in mind that O2 sensors are known to seize up and be a pain to extract. Arm yourself with patience and proper tools, and you should be good.
Can I Drive with a P0154 Error?
This is one of those trouble codes where it’s not a matter of can you drive with it present (you can), but rather should you? A bad O2 sensor will force your engine to operate under conditions that are anything but optimal.
While it’s perfectly fine to drive yourself home with this error present, you shouldn’t take extended drives or forget about the code altogether. We strongly recommend that you fix this issue as soon as possible.
Will P0154 Code Clear Itself?
Most O2 codes won’t usually clear themselves and will require you to clear them manually. Once you clear it, keep in mind that your car will have to go through several (usually three) complete driving cycles before the fix is confirmed. Don’t be surprised if you apply a fix and have the CEL come on after several days of driving.
Only Use Quality O2 Sensors
The O2 sensors in your car play a very important role in the way your car drives. As such, they are definitely the one component you don’t want to cut corners on. We strongly recommend using quality O2 sensors in your car as they can affect anything from performance to fuel consumption.
Here at eEuroparts.com, we offer a wide range of genuine and OEM sensors for all kinds of European vehicles. To find a sensor for your car, simply plug your car’s data into our vehicle selection tool and search for O2 sensors.


