Every gasoline engine needs three things to work — fuel, spark, and compression. When one or more of these elements are missing, you will experience issues. Or, like in the case of an ignition system failure, you’ll also get a check engine light code on the dash.
The particular code we’ll be talking about is the P0355 code. It’s a common error that comes up on all kinds of makes and models. The following guide should give you enough information to diagnose and potentially fix this code along with the issue that caused it in the first place. Grab your OBD-II scanner and settle in.

What is the P0355 Code, and What Does It Mean?
The P0355 fault code stands for “Ignition Coil “E” Primary/Secondary Circuit.” A simpler explanation would be that your PCM has logged an error with the ignition circuit assigned to the 5th cylinder of your engine. P0355 code belongs to a series of codes that range from P0351 to P0360, all of which are ignition circuit related.
That being said, this code doesn’t exactly point out which part of the ignition circuit is causing the issue. It’s merely telling you that there is a problem.
What Makes Up an Ignition Circuit?
Modern coil-on-plug ignition systems are slightly different from the older setups that have a single coil that feeds all cylinders through a distributor. With coil-on-plug systems, you essentially have the ignition coil, the spark plug, and the ECU(PCM).
The PCM is constantly monitoring the crankshaft and camshaft position sensors and uses that data to send spark instructions to each of the coils. The coil then fires up, charging the spark plug, which in turn creates a spark in the cylinder.
Alternatively, you may be dealing with an ignition coil pack, which is essentially a cluster of individual ignition coils. Both of these systems are not that difficult to diagnose. With distributor-based systems, you have to account for the additional components.
What Does Ignition Coil Primary/Secondary Circuit Mean?
The job of an ignition coil is to transform the low voltage battery power (12V) into high voltage (~20,000V) necessary to create a spark inside a cylinder. It does this by using two windings, or circuits — the primary circuit and the secondary circuit.
The primary circuit features a low number of windings, while the secondary features exponentially more — usually 100 times the number of windings on the primary circuit. When powered, these windings (or circuits) create a magnetic field.
Once the PCM issues a firing order to the ignition coil, the primary winding loses power, thus collapsing its magnetic field. This in turn creates a voltage spike in the secondary winding, where there are now 20,000 Volts being generated, ready to discharge straight into a spark plug.
When you read “Ignition Coil “E” Primary/Secondary Circuit,” these are the circuits they are talking about.
What Causes the P0355 Code?
Several things can cause a P0355 code, and most of them have to do with the ignition coil, the wiring/connectors, and the spark plug. If you have an issue with any of these components, you can expect this code to pop up.
These are the most common causes, but not the only ones. You will sometimes see a P0355 appear when there’s an issue with the ECU/PCM. Here’s a list of causes with the more common ones being at the top:
- Faulty ignition coil
- Ignition coil wiring issue
- Spark plug issue
- ECU/PCM issue
Faulty Ignition Coil
Ignition coils usually last a long time, often outlasting the vehicle itself. However, some makes and models are known for going through ignition coils more often than others.
Ignition coils fail for a number of reasons. The most common one is usually the heat. Being so close to the engine means that the ignition coil is exposed to massive amounts of heat as the engine gets up to speed.
Some ignition coil designs simply aren’t capable of properly handling these temperature changes in specific engines, which causes them to fail.
Ignition Coil Wiring Issues
Ignition coil wiring harness, including the connector, are two potential failure points that can cause ignition issues, and hence the P0355 code. Your ignition coil needs two things — 12V power and a signal from the ECU, so it would know when to open and close the circuit.
The signal line also happens to be the line that the ECU monitors to see if that particular ignition circuit is functioning properly. Any shorts in the signal line, or issues with the connector on this side, can cause the P0355 code to pop up on the dash.
Spark Plug Issue
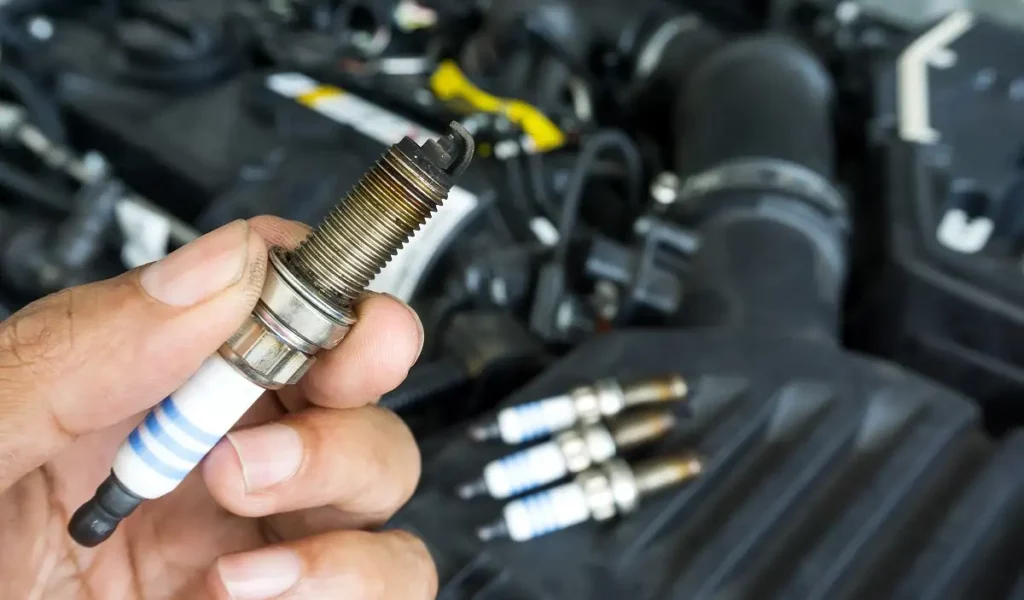

Faulty spark plugs are the second most common cause of the P0355 code. Every spark plug has a ground electrode and a side electrode.
The ground electrode is the one that runs through the middle of the spark plug, which is why it’s often called the center electrode. When this electrode shorts out and causes an open circuit, you could get the P0355 code on the dash.
Faulty PCM/ECU
Although incredibly rare, a faulty ECU/PCM can be the root cause of a P0355 error. Since there is a direct line between the ignition coil and the ECU, there is also a small chance that something on the ECU side of things has gone wrong.
If the ignition coil isn’t getting the right signal from the ECU, you’ll still get the same symptoms but no amount of parts that you throw at the car will fix anything until you replace the ECU/PCM.
What Are the Common Symptoms of P0355 Fault Code?
Unlike with other fault codes, the symptoms of a P0355 error are few. For the most part, this makes diagnosing the whole issue a fairly straightforward process since you know exactly where to focus your attention. Here are the two main symptoms you’ll run into:
- Check engine light
- Misfires
Check Engine Light
The very first symptom of a P0355 code is the activation of a check engine light. As soon as the ECU notices that something is off with the ignition coil on the 5th cylinder, you’re getting the code. This is good because you can run a scan and see exactly what’s going on in there.
Misfires
Engine misfire occurs when there’s no spark, fuel, or compression. If one or more of your ignition coils isn’t working properly, you’ll get misfires on the affected cylinders. Misfires can cause a slew of other issues. For example, a misfire can be intermittent, leading you to believe that something else is going on. Rough idling, increased fuel consumption and many others can all be a direct consequence of an engine misfire.
Lastly, if a cylinder is lacking spark, that means that all the fuel that enters said cylinder is dumped directly into the exhaust manifold where it can combust if the manifold is hot enough. Let this happen for long enough, and you’ll end up with a broken catalytic converter. And we all know that’s an expensive fix.
How to Diagnose and Fix the Cause of P0355 Code
Diagnosing the cause of the P0355 code comes down to taking a good look at the error logs from your OBD-II reader. Then, when you assess all the errors there, you can proceed to test every part of the ignition circuit that leads to cylinder No.5.
Full Scan of the Vehicle
First thing first, run a full scan of the car. For one, that’s the only way to know what code you’re dealing with, but also to see what other codes may be present. When a code appears completely alone, it means one thing.
When you see 4 different codes, all somehow related to each other, that can paint a whole different picture. Because of this, the first step should always be to run a full scan of the car.
Check the Ignition Coil
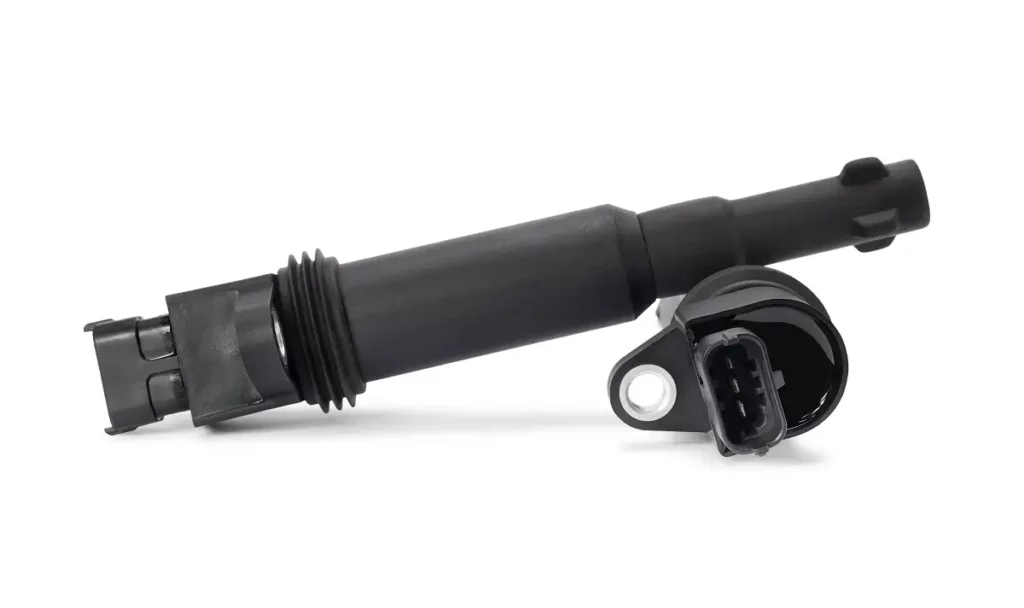

Testing an ignition coil can be done two ways — using a multimeter or by taking two ignition coils and switching their place.
With a multimeter test, the idea is to look for resistance in the coil by attaching the positive and negative probes to the two (or more depending on the design of the ignition coil) little terminals in the ignition coil.
The key is to prevent the two probes from touching at all costs. When you test the resistance of the primary coil, the values should be anywhere from 0.3 and 1 Ohm. If you see more than that, you might be dealing with a bad coil.
Before you go ahead and test the coil using a multimeter, make sure that you know what you’re doing. Some coils are so sensitive that you can damage them if you hook your multimeter to them the wrong way.
That being said, you can also take the ignition coil from cylinder number 5 and swap its place with another ignition coil. Once you do so, start the car and run a scan. If the problem has moved with the coil, you can be pretty certain that you’re dealing with a bad coil at which point you can go ahead and replace it.
However, if you’re still getting the P0355 code, that means that your issue is either with the spark plug or the wiring harness.
Inspect the Spark Plug
Spark plugs are a consumable item on any car, so it wouldn’t be too strange to find one that is bad or otherwise compromised.
Pull out the spark plug and examine the gap, as well as the center electrode. If you notice any excessive discoloration or other damage, go ahead and replace the spark plugs on your car. We recommend replacing all spark plugs at the same time.
Inspect the Wiring Harness
If the spark plug looks good, or you’ve changed it and the code keeps coming back, the next step would be to test the wiring harness. Before doing this, please understand that these instructions are for educational purposes only. Proceed at your own risk.
The reason for this disclaimer is simple — to test the harness you’ll need to probe it with a multimeter. If the two probes touch at any point while testing the harness, you run a risk of damaging your ECU.
That said, to perform this test, disconnect the cylinder 5 ignition coil harness from the coil. Take your multimeter, set it to voltage. Locate the power terminal on the connector (consult the manual for your car). Once you do so, connect your positive probe to the power terminal, and your negative probe to ground somewhere. With ignition on, and engine off, you should see battery voltage or 12V on the multimeter. If you don’t, you’ve got a wiring harness issue.
ECU/PCM Issues?
If none of the above yields any results, your last course of action should be a closer inspection of the ECU/PCM, whichever one is tasked with handling ignition in your car. Unfortunately testing these modules is a pretty complex task, but you still visually inspect them.
Check the ECU for water damage, and check to see if the connector has been compromised, or if there are any wiring issues on the backside of the connector. Any sign of damage on the ECU/PCM housing or connector can be a good indicator that it’s what’s causing the P0355 code.
Is It OK to Drive with P0355?
Driving around with a misfire is not something we can recommend. Can you do it? Yes, but you’re risking damaging your engine if you decide to drive around like that for any significant period of time.
That being said, it’s perfectly fine to drive the car home if you notice this issue, or to get it from home to the shop somewhere in case you’re looking to have someone fix it for you.
Solve the P0355 Code Using Quality Parts!
The best way to solve the P0355 code is to use quality parts to replace whatever’s broken. Here at eEuroparts.com, we offer a wide range of Genuine, OEM, and quality aftermarket ignition coils, spark plugs, and other parts you might need to get your car back on the road.
To find what you’re looking for, head over to our store, select your vehicle using our navigation tool, and you’ll be presented with a list of parts that are all guaranteed to fit your vehicle!


